I coined the term the White Death last year when attention finally turned to a remarkable fall in life expectancy among some white populations due to the lucky coincidence of economist Angus Deaton and his wife publishing a paper on the subject just days after he was awarded the new quasi-Nobel Laureate in economics.
From The Economist:

Illness as indicatorWell, it was pretty much of a secret until only a year ago.Local health outcomes predict Trumpward swings
Nov 19th 2016 | NEW YORK | From the print edition
… on November 15th Patrick Ruffini, a well-known pollster, offered a “challenge for data nerds” on Twitter: “Find the variable that can beat % of non-college whites in the electorate as a predictor of county swing to Trump.”
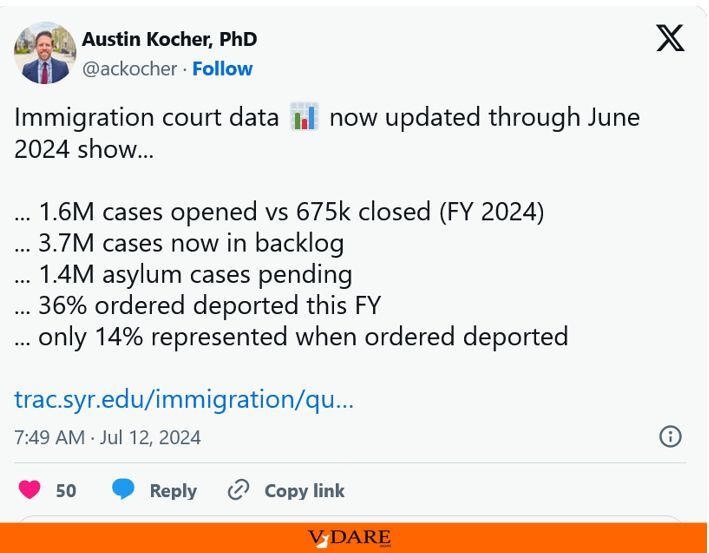
With no shortage of nerds, The Economist has taken Mr Ruffini up on his challenge. Although we could not find a single factor whose explanatory power was greater than that of non-college whites, we did identify a group of them that did so collectively: an index of public-health statistics. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington has compiled county-level data on life expectancy and the prevalence of obesity, diabetes, heavy drinking and regular physical activity (or lack thereof). Together, these variables explain 43% of Mr Trump’s gains over Mr Romney, just edging out the 41% accounted for by the share of non-college whites (see chart).
The two categories significantly overlap: counties with a large proportion of whites without a degree also tend to fare poorly when it comes to public health. However, even after controlling for race, education, age, sex, income, marital status, immigration and employment, these figures remain highly statistically significant. Holding all other factors constant—including the share of non-college whites—the better physical shape a county’s residents are in, the worse Mr Trump did relative to Mr Romney.
For example, in Knox County, Ohio, just north-east of Columbus, Mr Trump’s margin of victory was 14 percentage points greater than Mr Romney’s. One hundred miles (161 km) to the east, in Jefferson County, the Republican vote share climbed by 30 percentage points. The share of non-college whites in Knox is actually slightly higher than in Jefferson, 82% to 79%. But Knox residents are much healthier: they are 8% less likely to have diabetes, 30% less likely to be heavy drinkers and 21% more likely to be physically active. Holding all else equal, our model finds that those differences account for around a six-percentage-point difference in the change in Republican vote share from 2012.
The data suggest that the ill may have been particularly susceptible to Mr Trump’s message. According to our model, if diabetes were just 7% less prevalent in Michigan, Mr Trump would have gained 0.3 fewer percentage points there, enough to swing the state back to the Democrats. Similarly, if an additional 8% of people in Pennsylvania engaged in regular physical activity, and heavy drinking in Wisconsin were 5% lower, Mrs Clinton would be set to enter the White House. But such counter-factual predictions are always impossible to test. There is no way to rerun the election with healthier voters and compare the results.
The public-health crisis unfolding across white working-class America is hardly a secret.
Last year Angus Deaton, a Nobel-prize-winning economist, found that the death rate among the country’s middle-aged, less-educated white citizens had climbed since the 1990s, even as the rate for Hispanics and blacks of the same age had fallen. Drinking, suicide and a burgeoning epidemic of opioid abuse are widely seen as the most likely causes. Some argue that deteriorating health outcomes are linked to deindustrialisation: higher unemployment rates predict both lower life expectancy and support for Mr Trump, even after controlling for a bevy of demographic variables.I’m reminded of the horrifying drop in life expectancy in Russia during the Yeltsin years.
Polling data suggests that on the whole, Mr Trump’s supporters are not particularly down on their luck: within any given level of educational attainment, higher-income respondents are more likely to vote Republican. But what the geographic numbers do show is that the specific subset of Mr Trump’s voters that won him the election—those in counties where he outperformed Mr Romney by large margins—live in communities that are literally dying. Even if Mr Trump’s policies are unlikely to alleviate their plight, it is not hard to understand why they voted for change.In other words, as I’ve pointed out before, Trump voters tended to be civic-minded individuals doing okay themselves, but concerned about the trouble in their overlooked communities.